The Concept of Enneagram

What is Enneagram?
Enneagram finds its roots in the theories of ancient Greek mathematicians and philosophers. Enneagram means 9 points. (Ennea -gram) the nine personality types.
Modern-day Enneagram was developed on the foundation laid by George Gurdjieff in the 1900s. In 1970, Oscar Ichazo and Claudio Naranjo further developed this personality model. Enneagram hence is one of the oldest personality tests known and the most comprehensive and accurate modern-day personality assessment.

Unlike several popular personality tests, Enneagram is not a behavior-based assessment. It delves deep into our subconscious mind, taps into our core beliefs, motivations, and fear, and helps us understand the ‘why’ we do things and not just the ‘how’ we do it. Its modern-day application is not limited to knowing one’s personality type, but the journey of awareness, development, and awakening begins with knowing one’s core type. It is used to understand ourselves and our loved ones and shows how people see things differently. We can then see the world through 9 different lenses, significantly improve our emotional intelligence, and awaken ourselves!
Why is Enneagram useful?
The Enneagram is a helpful guide in the journey towards self-awareness, self-development, relationship building, conflict resolution, and improving team dynamics. However, it does not ‘box’ or stereotype people. An individual is more complex, unique, and distinct than the Enneagram type reflects.

Enneagram model delves deep into the different aspects of personality, such as core motivation, core fears, defense mechanisms, blindspots, vulnerabilities, passions, social style, conflict resolution style, the influence of other types, and survival instincts.
Specific suggestions and developmental ideas help liberate us from the traps of repetitive patterns and guide us to experience life more prosperous and mindful. Thus Enneagram gives us a more precise lens to look at the world!
Important Enneagram constructs
Enneagram can be better understood and appreciated through its following constructs.
1) Dominant type
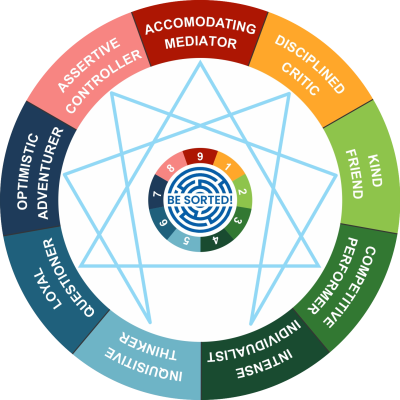
Enneagram suggests nine different personality types. Everyone is Ennea-Gram (9 types), a unique combination of 9 types. Though one Ennea type out of nine types is largely dominant and governs an individual’s perception of the world, responses, and behavior. The nine types are:
2) Survival instincts
Survival Instinct or gut instinct is based on our animal wisdom. The instinctual responses are automatic and fast, and we realize after acting on them. These are based on our biological drives for survival. Survival instinct could get activated as a defense mechanism when not needed. Survival instinct combines with our unique Ennea personality type to form new chemistry of our Type + Subtype (survival instinct type).
Survival instincts are A) Self Preservation, B) Intense Personal, and C) Social. Out of these three, one of them tends to be dominant, the second one is sometimes used and the third one is repressed.


Self Preservation
focuses on self-survival and well-being, safety, and security. This facet focuses on the tangible aspects of life, such as food and shelter. The focus is on making things permanent and secure. A person with this instinct values stability.

Intense Personal
focuses on a one-on-one relationship (You and me against the big bad world). The primary fear for this instinct is the fear of being unwanted. A sense of security is through a strong connection with someone. There is a creative impulse, a potent force, hence the intensity.


Social
focuses on the wellbeing and survival of the tribe, or herd. The fear is to not belong or find a place in the community. As a wolf survives only in a pack, the dominant social instinct makes one think for the whole group.
3) Centres of Intelligence
According to Enneagram, humans are three-brained beings and possess three centers of intelligence:
- the instinctual: the gut
- the feeling: the heart
- the thinking: the head
Types 2, 3, and 4 belong to the Heart center, and the underlying theme of emotions for this center is sadness, guilt, shame, etc. The language of this center is What do we know? What is the most efficient way to approach the problem?
Types 5, 6, and 7 belong to the Head center, and the underlying theme of emotions for this center is fear, and anxiety. The language of this center is how do the people involved feel about it? What is the deeper meaning of the problem?
Types 8, 9, and 1 belong to the Gut center, and the underlying theme of emotions is anger. The language of the center is What is the priority? What needs to be done? When do we start working on the problem?
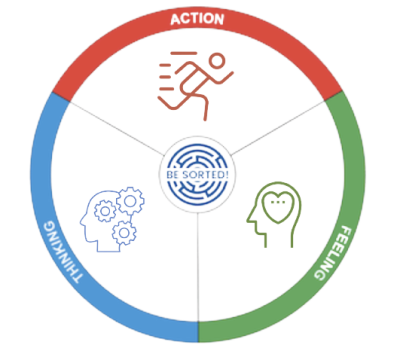

4) Centers of Expression
The center of expression is our behavioral style, how we show up in the world and express ourselves. This helps us understand which centers are expressed clearly, which centres are under-expressed, and how we process information. Our dominant center of expression explains our modus operandi.


Action First
People with high action centre are energetic, who focus on making things happen. They evaluate priorities and focus on getting started and getting things done. Their gut instinct is usually well developed, are decisive and are quick to act. When action is supported by feeling, the expression is Intuitive, instinctual, focus on people and their feelings. When action is supported by thinking, the expression is Intuitive, instinctual, focus on facts, data and consequences.


Feeling First
People with high feeling centre are emotionally intelligent, self-aware, effectively build strong relationships with people. Their focus is on how will people feel about a situation. When feeling is supported by action, the expression is Impulsive, collaborate to get things done, may neglect facts. When feeling is supported by thinking, the expression is Strategic, informed approach, have diverse perspectives.


Thinking First
People with high thinking centre focus on efficiency. They consider facts, analyze and move to action and minimize subjectivity. When thinking is supported by feeling, the expression is Diverse perspectives, rational approach, take into account people's opinions. When thinking is supported by action, the expression is Strategic, informed approach, people's feelings might get neglected.
5) Wings

The two adjacent types of the dominant type are known as wings in the framework of Enneagram. For example, if the dominant or core type is 3, 2 and 4 are the wings. Enneagram experts observe that either of the wings has an influence of their characteristics on the dominant type. Wings are used to chart out individualized growth plan through Enneagram.
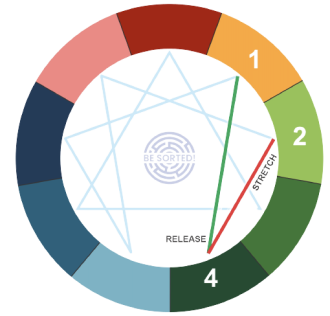
6) Lines
When a person is in a stable state of mind, and are peaceful, they move from their home type or the core type on the line of another type, as shown in the figure. This line is known as line of release. It feels very natural for a person to take up characteristics of the point of release. The person takes on the positive aspects of the point of release type. Eg. Line of release for type 4 is type 1. When emotionally stable, a Ennea 4 becomes disciplined, structured, and focuses on doing the right thing.
Similarly, during distress, a person moves from the home of core type to the point of strain. It is not a comfortable place to stay long in the point of strain. During distress, a person takes up the negative aspects of the point of strain. E.g. When emotionally upset, Ennea 4 becomes needy, self-absorbed, and manipulative (the negative traits of type 2).
Each core type has a line of release and a line of strain.